So you've decided that the meeting or workshop you have in mind needs an independent, professional facilitator. You call them up and guess what? They start asking all these awkward questions. What's that about?
Facilitators don't just turn up and facilitate
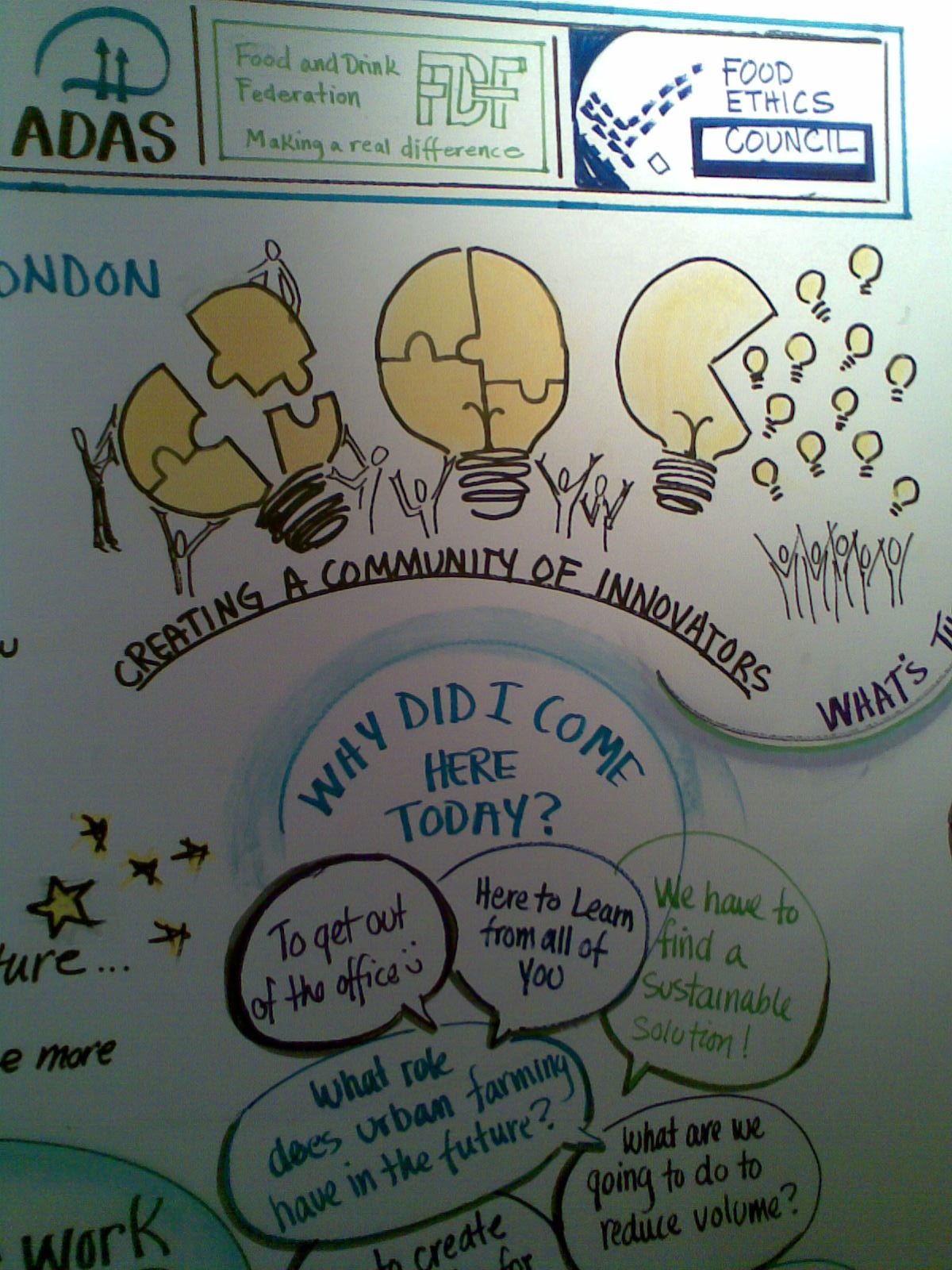
Facilitated meetings are increasingly popular, and many teams and project groups understand the benefits of having their workshop facilitated. More and more organisations are also wanting to have meaningful, productive conversations with stakeholders, perhaps even deciding things together and collaborating. Facilitated workshops can be a great way of moving this kind of thing forward. But facilitators don't just turn up and facilitate. So what are the key things a facilitator will want to know, when they're trying to understand the system, before the big day itself?
Start with the ends
Your facilitator will always begin with the purpose or objectives - why is the meeting being held? What do you want to be different, after the meeting? This could be a difference in the information that people have (content), new agreements or decisions (process), or it could be that what is needed is a shift in the way people see each other (relationships) - or some of each of these things.
Context and history
Once the facilitator is confident that you are clear about the purpose (and this could take some time - the facilitator should persist!), then the facilitator will want to understand the context, and the people.
Context includes the internal context - what has you organisation done up to now, what other processes or history have led up to this workshop? It also includes the external context - what in the outside world is going to have an impact on the people in the room and the topic they are working on?
Who's coming?
Often, the one thing that has been fixed before the facilitator gets a look in is the people who have been invited. But are they the right people to achieve the objectives? Have some important oilers or spoilers, information holders or information needers been left out? And do they understand clearly what the objectives of the meeting are?
Getting the right people in the room (and making arrangements to involve people who need to take part, but can't actually be there on the day) is just part of it. What do the people need to know, in order to play an effective part in the meeting? And how far ahead does this information need to be circulated? Apart from passively receiving information, what information, views or suggestions can be gathered from participants before the meeting, to get people thinking in advance and save time for interaction and creative discussion on the day? What questions can be gathered (and answered) in advance?
What do the participants want out of the meeting? If this is very different to what the client or sponsor wants, then this gap of expectations needs to be positively managed.
When and where?
Apart from the invitation list, the other things which are usually fixed before the facilitator is brought in, and which they may challenge, with justification, are the date and the venue.
The date needs to be far enough away to ensure that participants get adequate notice, and the facilitator, client team and participants get adequate preparation time.
The venue needs to be suitable for the event - and for a facilitated meeting, traditional conference venues may not be. Inflexible room layout, a ban on blu-tack, rigid refreshment times - all of these make a venue hard to use, however handy it may be for the golf course. There's more on venues here.
Workshop design
Sometimes, of course, the date, venue and participant list are unchangeable, whatever the facilitator would like, and have to be taken as fixed points to be designed around. So what about the overall meeting design? The facilitator will want to understand any 'inputs' to the meeting, and where they have come from. They'll want to talk about the kind of atmosphere which will be most helpful, and about any fixed points in the agenda (like a speech by the Chief Exec), and how these can be used most positively.
A design for the meeting will be produced, and circulated to key people (the client, maybe a selection of participants), and amended in light of their comments. But the facilitator will always want to retain some flexibility, to respond to what happens 'in the room'.
What next?
And after the meeting? The 'after' should be well planned too - what kind of report or record is needed, and will there be different reports for different groups of people? This will have an impact on the way the meeting is recorded as it goes along - e.g. on flip chart paper, on display for all to see and for people to correct at the time. If there are specific 'products' from the meeting (agreements, action points, priorities, principles or statements of some kind, options or proposals), what is going to happen to them next?
And how will the client, facilitator and participants give and receive feedback about how the process worked?
All these things will need to be thought about early on - clients should expect their facilitators to ask about them all - and to help them work out the answers!
Challenging conversations
So to sum up, the facilitator will potentially challenge the client team about:
• Objectives • Context • Participants • Space • On-the-day process • Follow-up process
Free download
If you'd like to download a version of this, click here.